How To Get Residency in Cambodia: A Comprehensive Guide
Capital: Phnom Penh
Population: 17,638,801 (2024, 71st)
Ethic Group: 95.8% Khmer,1.8% Cham
Area: 181,035 km2 (88th)
Offical Language: Khmer
Currency: Riel (៛)
GDP per Captial: $6,541 (2024, 144th)
Human Development Index: 0.606 (2023, 151st)
Country Profile:
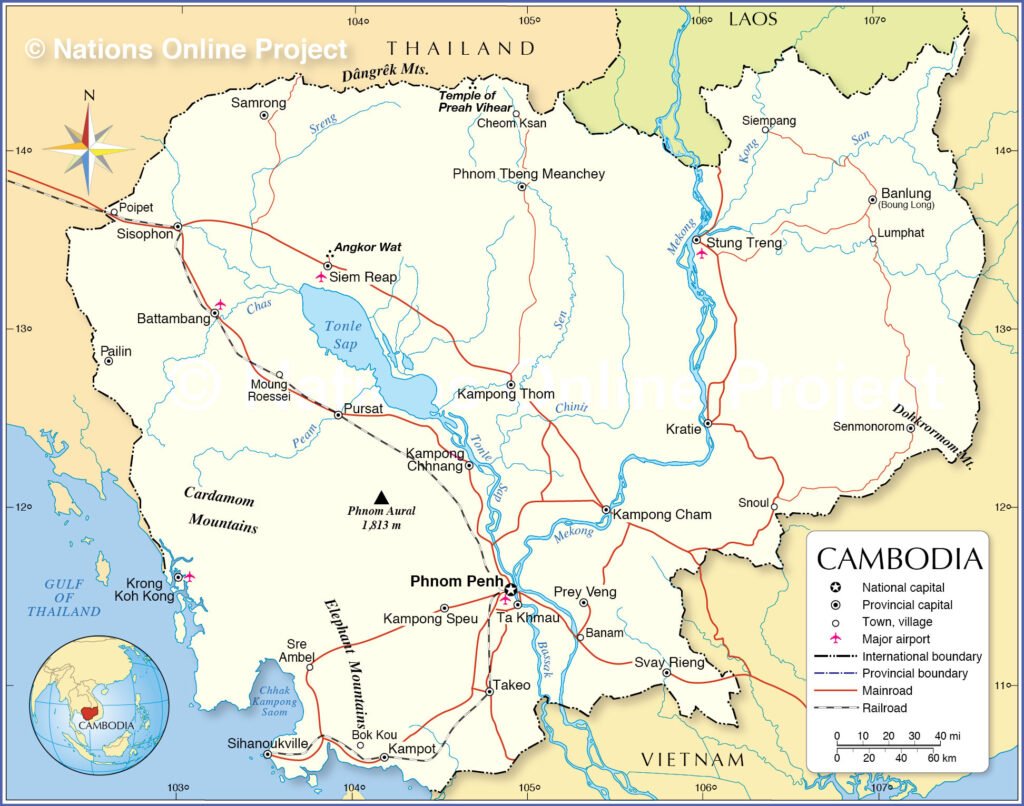
Cambodia is a constitutional monarchy located on the Indochinese Peninsula in Southeast Asia and is recognized by the United Nations as one of the world’s least developed economies.
Economically, Cambodia is primarily agricultural, with major crops including rice, rubber, corn, and palm sugar. In recent years, tourism, garment manufacturing, and construction have also become important components of the national economy.
Historically, Cambodia was known as the Khmer Empire, an ancient civilization with a long history. As the center of the ancient Khmer Empire, Angkor Wat and other historical sites attract a large number of tourists to Cambodia every year.
Visa & Immigration System:
What many don’t realize is that Cambodia is theoretically one of only ten countries globally offering citizenship by investment programs. In theory, foreigners who donate 1 billion Cambodian Riel (approximately $245,000 USD) or invest 1.25 billion Cambodian Riel (roughly $300,000 USD) are eligible to directly obtain Cambodian citizenship through a passport program.
However, in practice, due to the local government’s inaction and a significant lack of transparency, this passport program is largely defunct. Investors find it nearly impossible to successfully apply for Cambodian citizenship through this route.
Currently, Cambodia’s only genuinely viable investment immigration program is its My Second Home Program. This initiative grants a ten-year Cambodian residency permit to foreign investors who put $50,000 USD into government-listed real estate projects and pay an additional $50,000 USD for a ten-year MySH membership fee, totaling a $100,000 USD outlay.
A significant advantage of the MySH program is its accelerated path to citizenship. Participants who have legally resided in Cambodia for five years become eligible to apply for naturalization through a fast-track process, compared to the standard seven-year residency requirement for those applying via normal channels.

Beyond these two specific investment immigration programs, Cambodia’s visa system is quite comprehensive, including:
- B-class work visas
- C-class visitor visas
- E-class ordinary visas
- K-class visas for former Cambodian citizens visiting relatives
The E-class visa category itself encompasses several mainstream options such as:
- EB-class business visas
- EG-class job-seeking visas
- ER-class retirement visas
- ES-class student visas
Among these, the ER-class Cambodian retirement visa has become particularly popular in recent years. Its simple entry requirements, convenient application process, affordable cost of living, and Cambodia’s exotic charm have made it an increasingly sought-after option for retirees looking to settle abroad.
Currently, the Cambodian government’s criteria for issuing retirement visas remain quite flexible. Generally, if your income can consistently meet or exceed $500 to $1,000 USD per month, you’ll likely qualify for a Cambodian retirement visa.
Dependents:
For most Cambodian immigration visas, the main applicant’s spouse and minor children can also relocate to Cambodia as dependents.
Citizenship:
Foreigners are eligible to apply for Cambodian citizenship after legally residing in the country for seven years and meeting other specified conditions.
Passport Power:
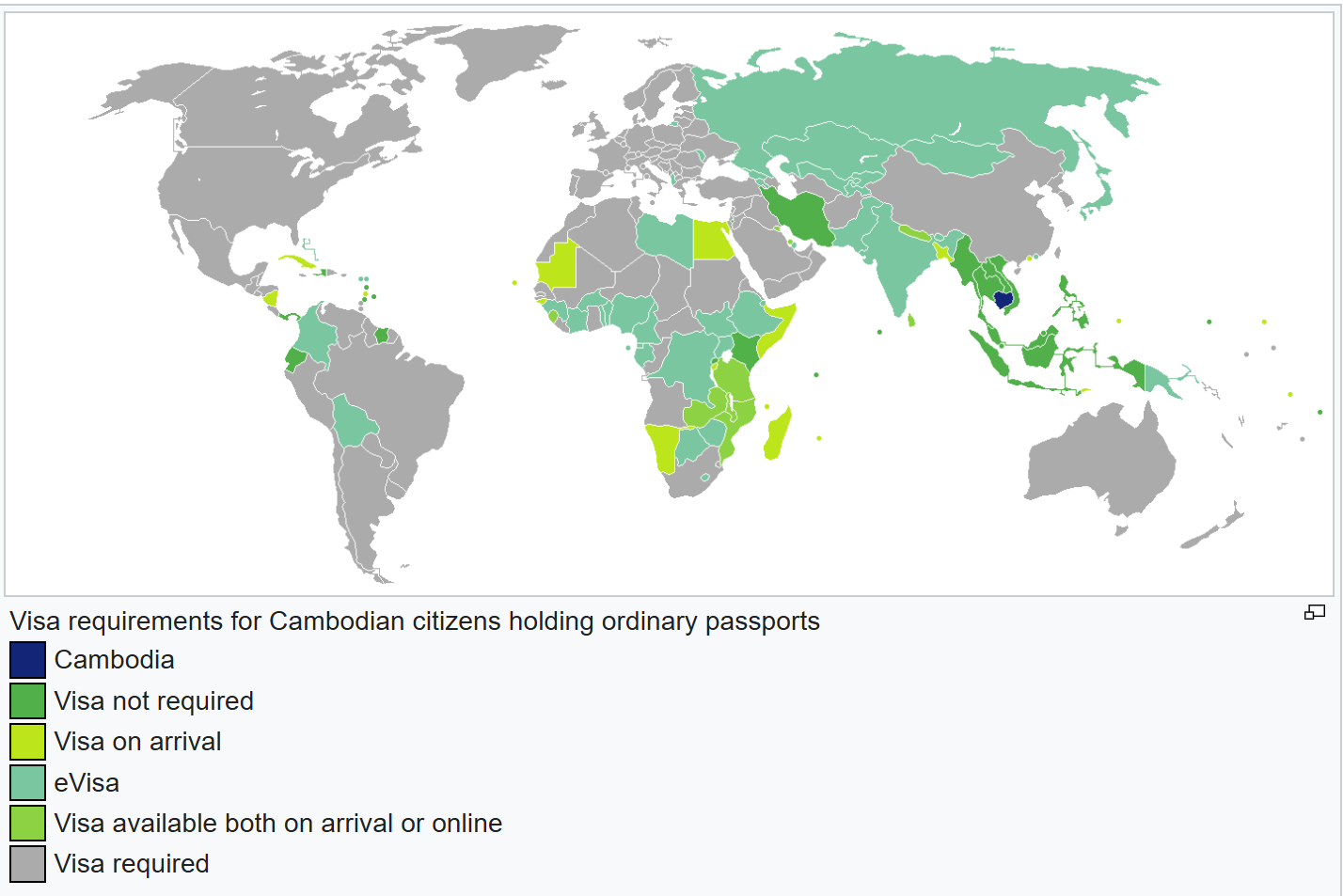
Cambodia allows dual citizenship, and its passport is ranked 86th globally. Cambodian citizens enjoy visa-free or visa-on-arrival access to 52 countries and territories worldwide. None of these visa-free countries are traditional western countries. (June 10th, 2025)
Useful Links:
Cambodia Ministry of Interior:https://www.interior.gov.kh/
The Development of Cambodia Council: https://cdc.gov.kh/
Cambodia Second Home Program: https://cm2h.com/