Home > Africa > South Africa > How To Get Residency in South Africa | A Complete Guide
How To Get Residency in South Africa | A Complete Guide

Country Profile:
South Africa, nestled at the southernmost tip of Africa, is a member of both the G20 and the Commonwealth. It stands out as one of the most ethnically and culturally diverse nations in Africa and globally.
This country boasts a rich and varied landscape, from vast grasslands to stunning coastlines and iconic mountains like Table Mountain. It’s also a world-renowned destination for wildlife viewing, with Kruger National Park alone drawing countless visitors.
Economically, South Africa plays a significant role on the African continent, featuring well-developed infrastructure in finance, communication, energy, and transportation. However, it grapples with considerable challenges, including wealth disparity and social inequality.
Visa & Immigration System:
South Africa stands out as one of Africa’s most open countries for immigration, offering a variety of long-term residence permit options for foreign nationals.
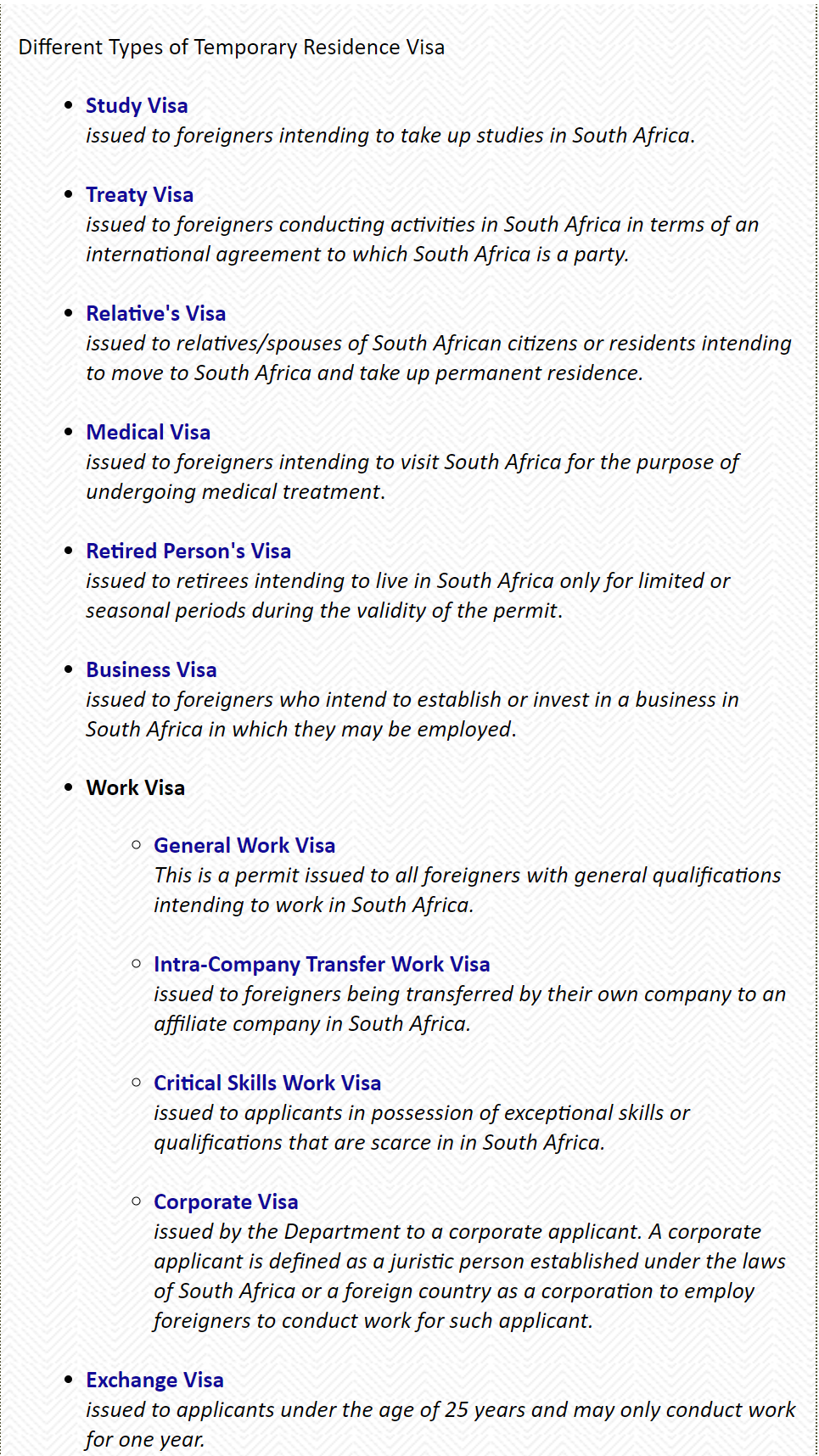
Some of the most common South African residence permits include:
1. Financially Independent Permanent Residence Permit (27F Visa):
This visa is for those who can demonstrate a net worth of at least 12 million South African Rand (approximately $690,000 USD) and are willing to make a one-time donation of 120,000 South African Rand to the South African government after the visa is approved.
The Financially Independent Permit is a once-off permanent residence visa. Holders are free to study, work, conduct business, and live in South Africa. There’s no requirement for continuous physical residence; you simply need to enter South Africa once every three years to maintain your permanent resident status.
2. Retirement Visa:
Compared to Financially Independent Permit, the South African Retirement Visa’s primary requirement is income-based: you qualify if you can prove a monthly income of 37,000 South African Rand (approximately $2,100 USD).
This income isn’t limited to a pension; it can include rental income, interest from savings, dividends, or any other non-employment income. Importantly, there are no age restrictions for applicants of the South African Retirement Visa.
However, if you apply for this visa, you are not permitted to engage in any work or business activities in South Africa; you can only spend money within the country.
3. Business Visa:
This visa is issued to individuals who invest at least 5 million South African Rand (approximately $283,000 USD) to establish or acquire a company in South Africa and engage in business operations.
To qualify for this visa, your company must also create jobs, and over 60% of your employees must be South African citizens or permanent residents.
4. Work Visas:
South African work visas include four types: corporate visas, intra-company transfer(ICT) work visas, critical skills work visas, and general work visas. The basic prerequisite for obtaining a work visa is having the support of a local employer.
Work visas generally have a maximum validity of 5 years, and a critical skills worker in key industries may have the possibility to directly apply for permanent residency in South Africa.
5. Digital Nomad Visa:
The South African government announced plans to launch a Digital Nomad Visa program for remote workers in April 2022. However, as of now, the specific details regarding this visa have not yet been released.

Dependents:
For most South African immigration visas, the following individuals can be included as dependents on the main applicant’s visa:
-
The main applicant’s spouse or a partner with whom they have been in a continuous relationship for at least five years.
-
Unmarried children under the age of 21.
-
Children of any age who have a physical or mental disability.
Permanent Residency & Citizenship:
South African permanent residence permits are categorized into two main types: Direct Permanent Residence and Residence permit on another basis.
Residence permits on another basis are primarily issued to individuals on financially independent permit, refugees, highly skilled workers in critical sectors, and investors in the country. Among these, the first two categories (financially independent and refugees) account for the largest number of permits issued.
Direct Permanent Residence permits are granted to foreign nationals who have legally resided in South Africa for a continuous period of five years.
After obtaining permanent residency, individuals become eligible to apply for naturalized South African citizenship once they have resided in the country for an additional five years.
Passport Power:
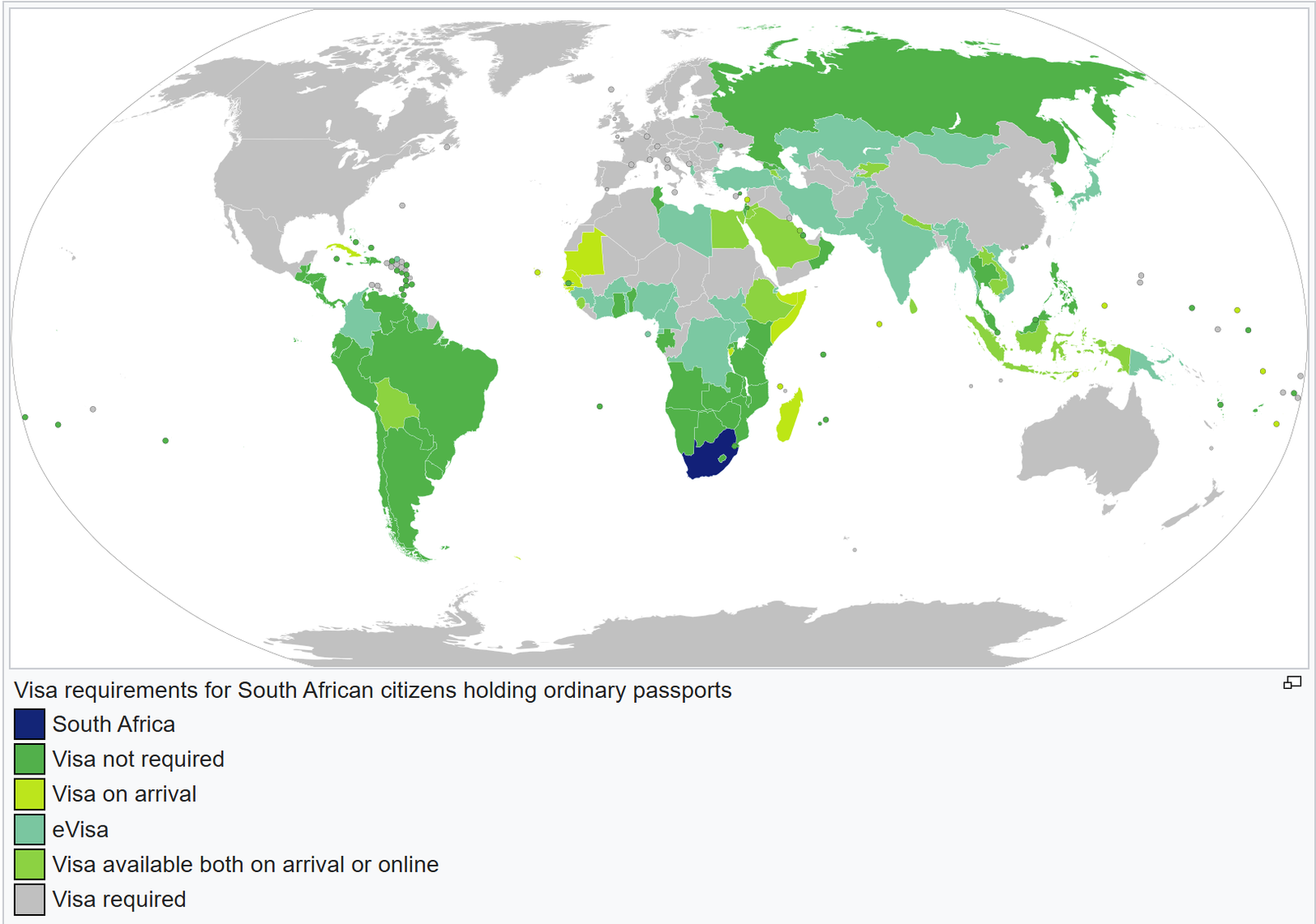
South Africa recognizes dual citizenship, and its passport ranks 49th globally. Holders of the passport can travel freely (either visa-free or obtaining a visa on arrival) to 104 countries and regions around the world. (As of July 3, 2025)
Useful Links:
The Department of Home affairs Of South Africa:http://www.dha.gov.za/index.php/immigration-services
South Africa Permanent Residency:https://www.southafrica-usa.net/homeaffairs/immigration.htm#:~:text=Section%2027(f)%20refers%20to,a%20retirement%20account
South Africa Retirement Visa:https://www.southafrica-usa.net/homeaffairs/permit_retired.htm
Home > Africa > South Africa > How To Get Residency in South Africa | A Complete Guide